This test-rig demonstrates the feasibility of using pressurised air as lubrication to reduce the friction losses. The air is injected through controllable smart material injectors, and due to the low viscosity of the air, the operation is almost friction free. This comes at the cost of poor damping properties making the machine sensitive to vibration. The shaft vibrations are measured to generate control signals to the smart material actuators and thereby enhance the damping and reduce the sensitivity to disturbances.
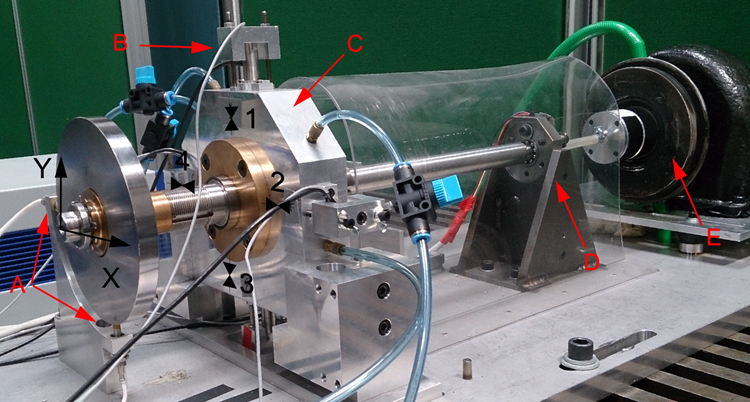 |
| The controllable gas bearing test rig. The shaft is supported by a ball bearing (D) and the controllable gas bearing (C), in which four piezoactuators (B) control the injection of air to keep the rotor levitated. The shaft is driven by a turbine (E), and the shaft vibration is measured with position sensors (A), and used for feedback to control the injection of air. The control enhances the damping and thereby reduces vibrations. |